The cell nucleus is one of the most important organs of a eukaryotic animal cell. It contains the DNA (genetic information) for replication and proteins synthesis. The nucleus is also responsible for the regulation of the cell.
The cell nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear envelope, which regulates what goes in and out of the nucleus. Inside the nucleus are chromosomes, which are made up of DNA. The DNA carries information for growth and reproduction.
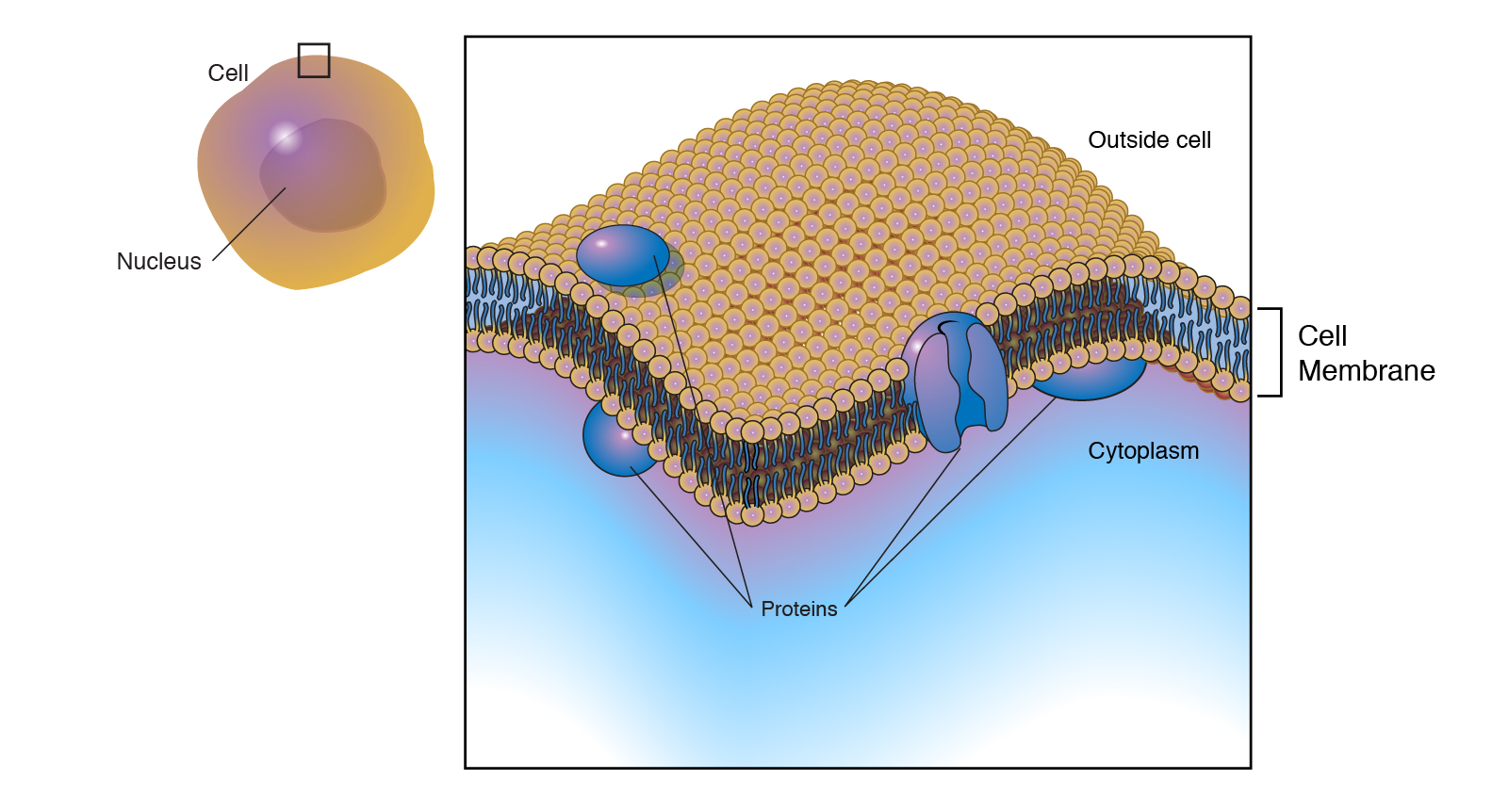
Cell membrane
The cell membrane is a selective barrier thatseparates the cytoplasm from the environment. It is also known as the plasma membrane or outer cell membrane. The cell membrane consists of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins. It is composed of two layers of phospholipids, which are arranged in a mosaic pattern.
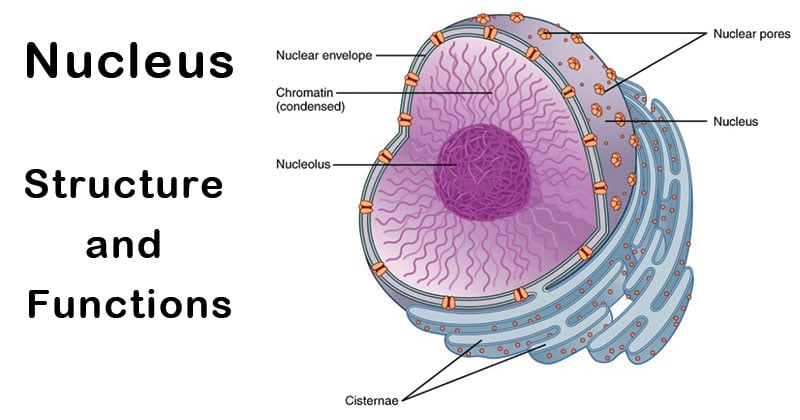
parts of nucleus and their functions
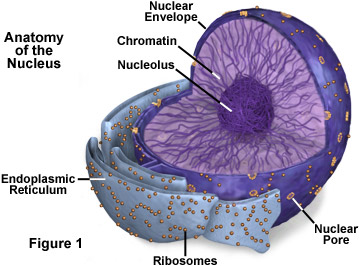
The nucleus is a large organelle that contains most of the cell's genetic material. The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus and separates it from the rest of the cell. The nuclear envelope is made up of two membranes: an outer membrane and an inner membrane.
The space between the two membranes is called the perinuclear space. The nuclear envelope is permeable, which means that small molecules can pass through it. The nucleus contains chromatin, which is made up of DNA and proteins. The DNA in chromatin is responsible for encoding the genetic information of a cell. The proteins in chromatin help to package the DNA and keep it organized. Chromatin is organized into chromosomes during cell division.
The nucleus also contains a number of smaller organelles, such as nucleoli and nuclear pores. Nucleoli are responsible for manufacturing ribosomes, which are used to produce proteins. Nuclear pores are membrane-bound channels that allow molecules to move in and out of the nucleus.
nucleus function
The main function of the nucleus is to store the cell's genetic material. This material is composed of DNA and controls the cell's growth and reproduction. The nucleus also plays a role in protein synthesis and cell division. Other important functions of the nucleus include regulating the cell's metabolism and controlling gene expression.
nucleus definition biology
The cell nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells. Eukaryotes usually have one nucleus, but a few types of cells, such as mammalian red blood cells, lack a nucleus.
The main function of the nucleus is to store the cell's genetic material. The cell nucleus contains most of the cell's DNA, which is organized into chromosomes. The nuclear envelope encloses the nucleus and separates it from the rest of the cell. The nuclear envelope consists of two membranes: an inner membrane and an outer membrane.
The nucleolus is a sub-organelle of the nucleus that helps to produce ribosomes. Ribosomes are small organelles that play a role in protein synthesis. The nuclear envelope is important for keeping the contents of the nucleus separate from the rest of the cell. It also helps to regulate what goes in and out of the nucleus.
Comments
Post a Comment